
Groundwork London’s CIRCLE programme works with refugees through employment support, language trainings and community events, to help finding employment and assist with socio-economic integration. The GDS team supports the programme by providing a customized CRM system, using the Zoho platform, to enable efficient data capturing and storing. Through the en-suite application the programme can store its data in a secure cloud environment, as well as managing its daily activities. By having all the information available in one place the programme can provide more efficient support to its clients and be better organized in its work. The application also provides powerful data analytics to give instant overviews of the programme’s performance for easy and fast reporting and data visualization. Zoho Analytics supports SQL driven reporting that lets you import data from a range of different sources and link with your own CRM systems. For CIRCLE we used Zoho Analytics to create a number of dashboards that are syncronized with the main application to display particpant information and keep track of the progaramme's performance. Through SQL based queires the data can be grouped and filtered to get the users specific reporting needs. Zoho Analytics also supports a range of different visualzations tools that brings life to your data. See below for an example of a dashboard with selected graphs created for the CIRCLE applicaiton.

The LiDAR is supplied as either a DSM (Digital Surface Model) or a DTM (Digital Terrain Model). For flood modelling, a DTM is most suitable as this covers the bare earth i.e excludes buildings and vegetation. To download the data you need to use the web portal located here. The LiDAR is supplied in 5km2 chunks in the ASCII file format. Use the composite DTM rather than the time stamped tiles. To work with the data in ArcGIS we need to transform it into a raster using the ASCII to Raster tool which can be found in the Arc Toolbox under Conversion -> To Raster -> ASCII to Raster. Be sure to change the ‘output data type’ from integer to float.
Once you have converted all your ASCII files to Raster you will need to merge the results into one final raster. This is achieved through the Mosaic to New Raster tool found under Data Management -> Raster -> Raster Dataset -> Mosaic to New Raster. Use the following parameters:
Input Location: Select the rasters to merge
Output Location: The folder where you want to save the output raster
Spatial Reference: British_National_Grid
Number of bands: Always one
Other inputs: leave as default
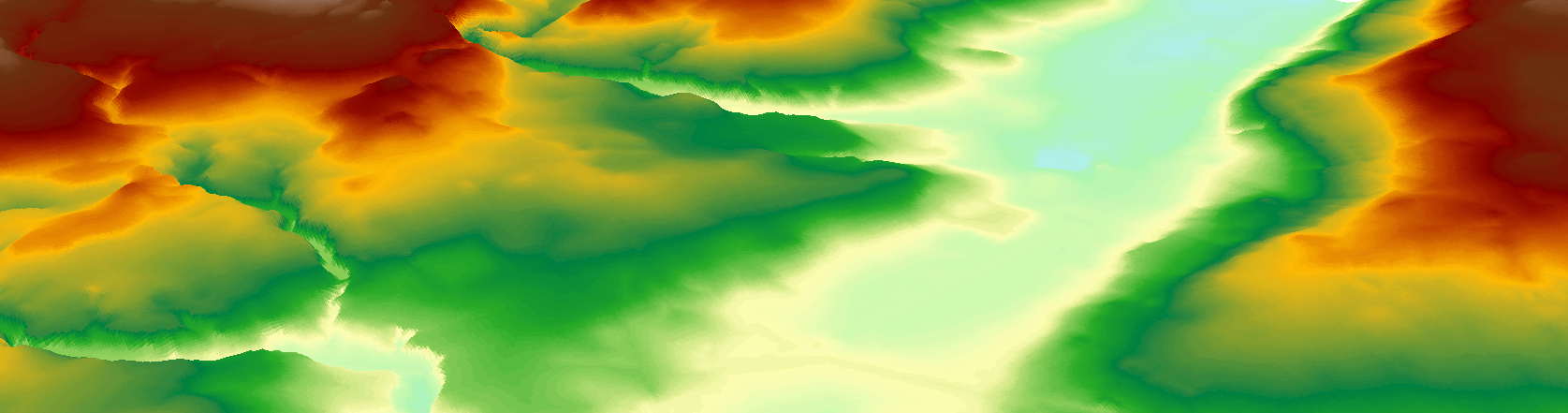
You can now visualise your DTM in ArcScene which gives a 3D overview of the data. This can be accessed from the 3D Analyst Toolbar in ArcMap. Add the layer we have just created into the Table of Contents, by default no height values are shown. To add in the 3D or Z component go to Layer Properties -> Base Heights -> Floating on a custom surface. Use the Z factor 'Factor to convert layer elevation values to scene units’ to show a greater delineation of the elevation - the higher the value the greater the height exaggeration.
Groundwork GDS is part of Groundwork London